ARGOS
All-in-one sensor monitoring cerebral activity during general anesthesia to preserve brain function of patients.
Home - ARGOS platform
INTEGRATED EEG & NIRS MONITORING PLATFORM
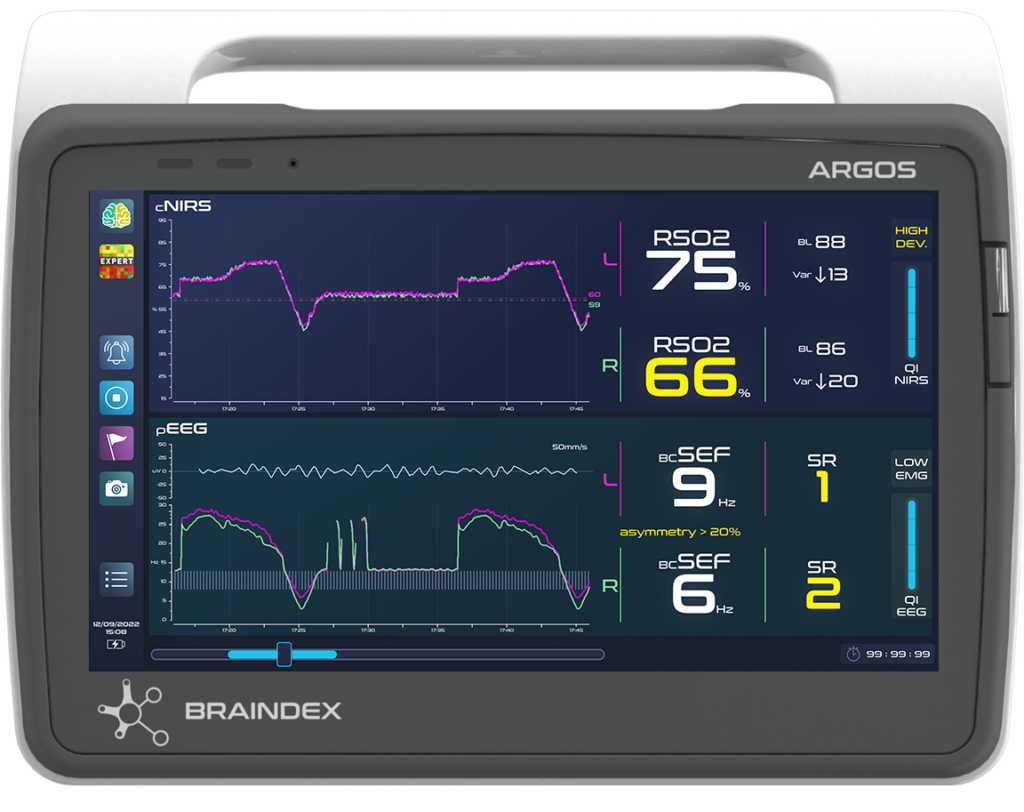
During surgery, ARGOS provides clinicians with unrivalled clinical data to assess the state of brain function in anesthetized patients.
By combining EEG and NIRS measurements, the ARGOS integrated platform enables clinicians to simultaneously, continuously, non-invasively and in real time assess the balance between brain oxygen supply and demand, as well as the degree of spontaneous cortical activity during general anesthesia.
ARGOS thus helps clinicians personalize anesthesia care to optimize post-operative patient outcomes, such as maintaining the integrity of neural and neurocognitive functions.
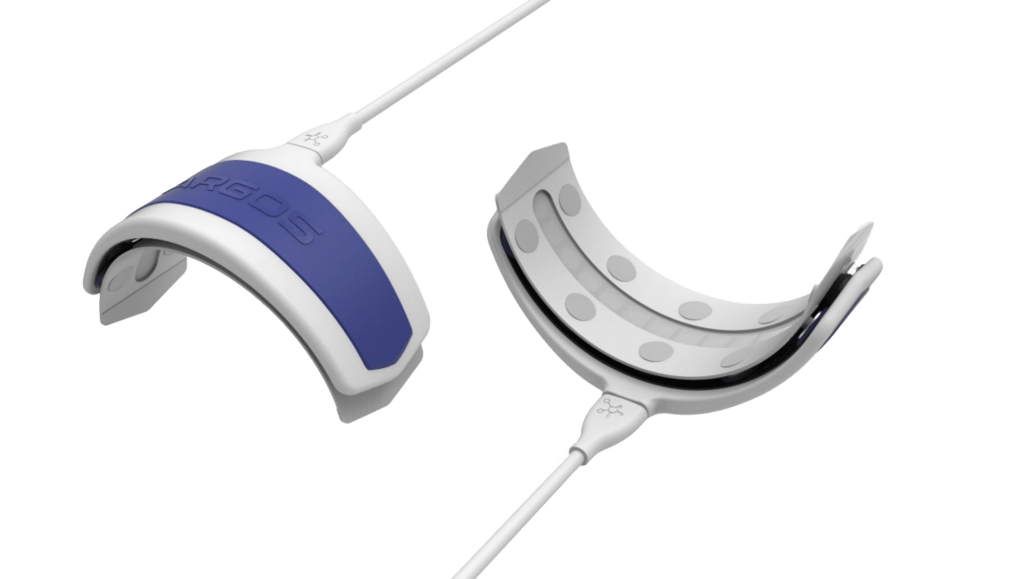
ALL IN ONE REUSABLE SENSOR

Interview of Prof. Julien Amour TAVI protocol
ADVANCED CEREBRAL NIRS
ARGOS reusable sensor combines 6 leds at 6 wavelengths each with 8 photoreceptors accounting for 144 optical vectors.
ARGOS offers unrivalled chromatic and spatial resolution for improved cortical selectivity of oxygen measurements along with greater fronto-temporal sample volume.
Since light propagation in biological tissue is a question of distance, the variability in the shape of patients’ skulls, which leads to variations in the distances between the sensor’s optical elements, creates a systematic bias in cortical oxygen measurements if not compensated for.
ARGOS patented adaptive optical footprint, based on 3 integrated tri-axial accelerometers, compensates for skull shapes, and maintains the reliability of cerebral oxygen measurements from patient to patient.
ARGOS NIRS algorithms are the first of their kind to be calibrated under surgical conditions, based on a clinical database created during TAVI (transcatheter aortic valve replacement).

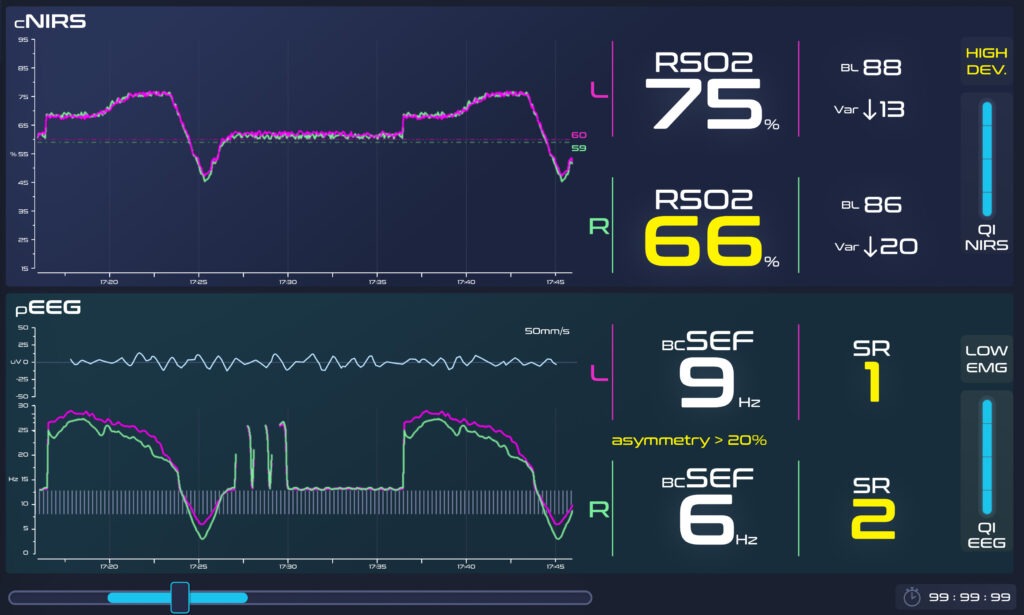
PROCESSED EEG
30 years after the inception of intraoperative EEG monitors designed to indicate the level of consciousness of patients under general anesthesia, the complexity of the neurological construct associated with general anesthesia has dispelled the idea of a simple index of consciousness, easily measurable under the influence of a variety of anesthetic states and transitions.
At the same time, EEG bursts suppression is recognized to reflect episodes of oversedation associated with postoperative neurological disorders.
ARGOS thus provides clinicians with a disclosed and understandable sedation index (burst compensated Spectral Edge Frequency – bcSEF) combined with the EEG burst suppression ratio (SR) to guide sedative administration and prevent adverse neurological effects associated with over-sedation.
DISPLAY MODES
The ARGOS human-machine interface has been designed to adapt to the wide variety of clinicians’ practices, enabling confident and optimized clinical decision-making to individualized anesthesia care.
from regular bimodal EEG-NIRS to optional trimodal EEG-NIRS-ANI (MDoloris)
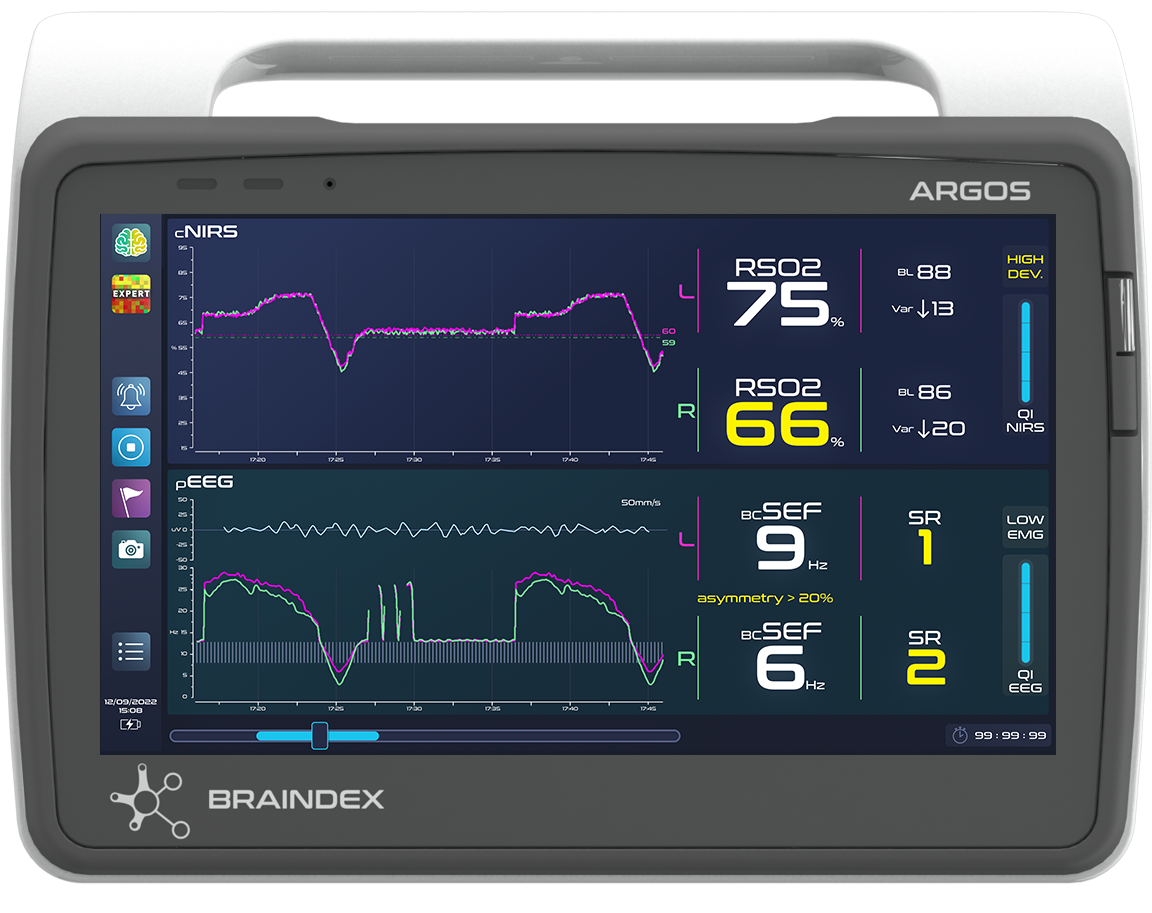
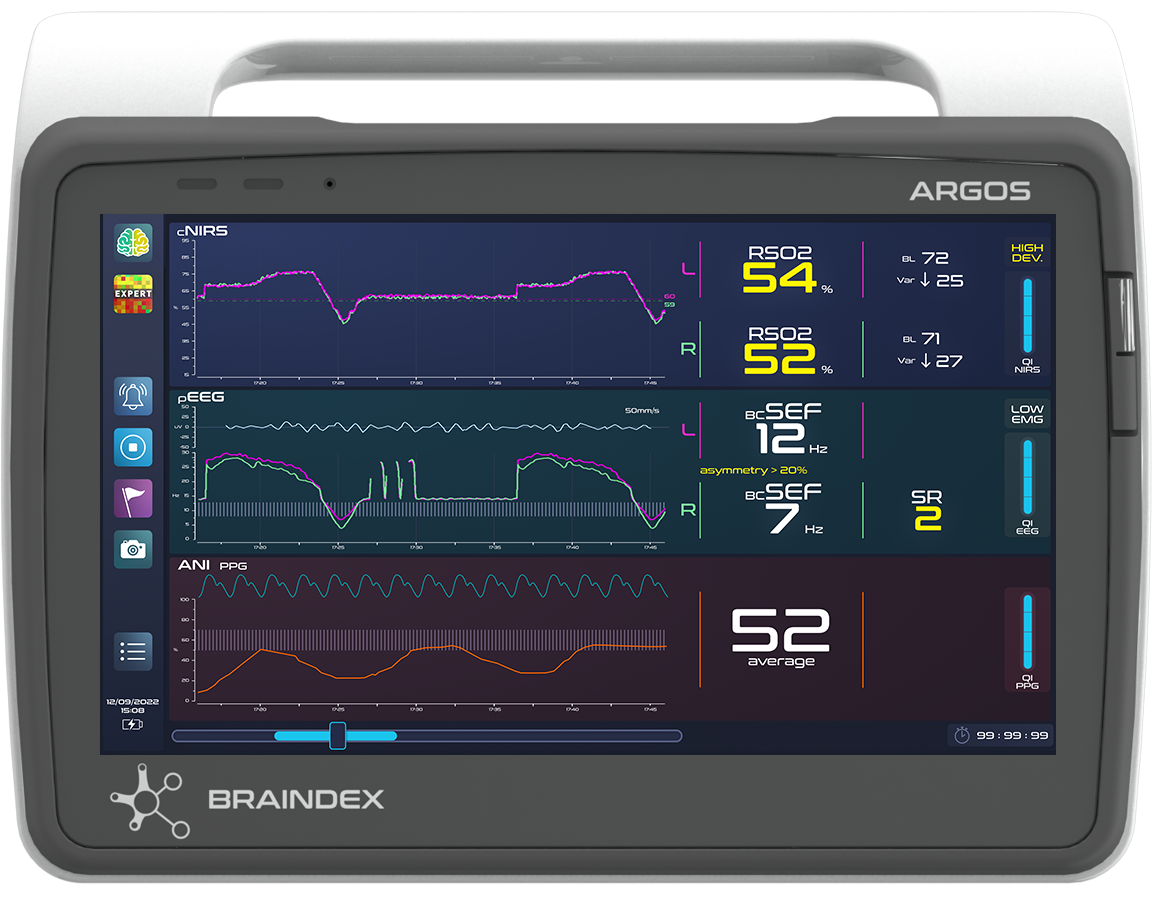

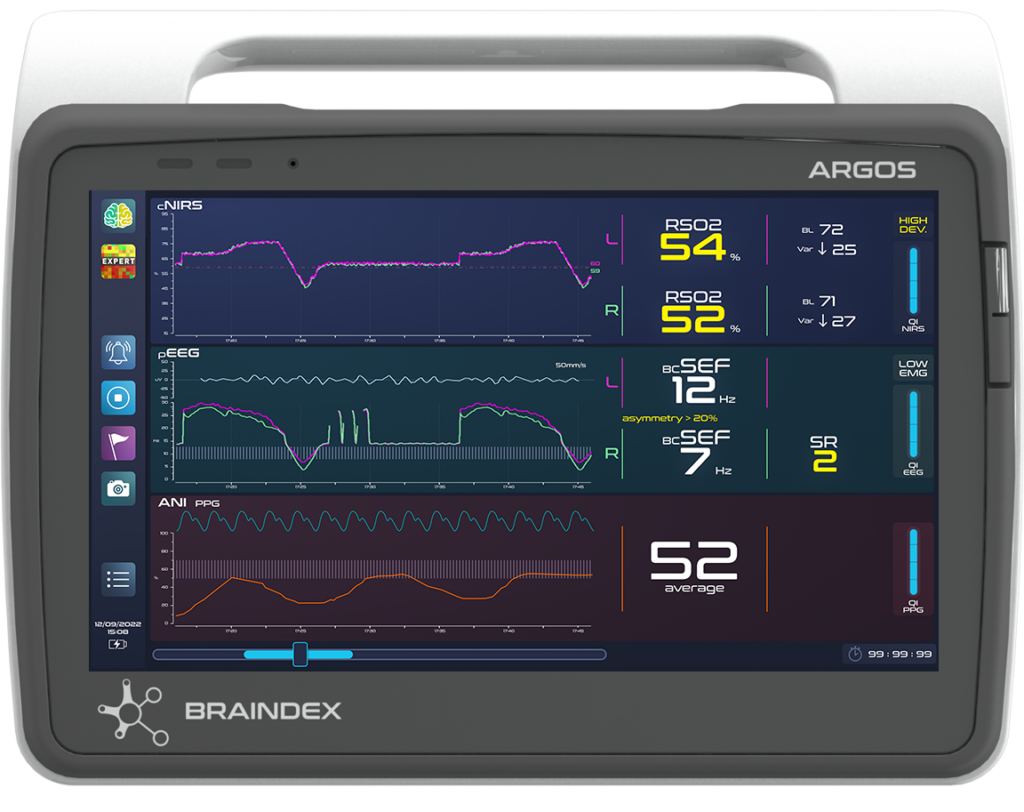
from basic to expert clinical decision support,

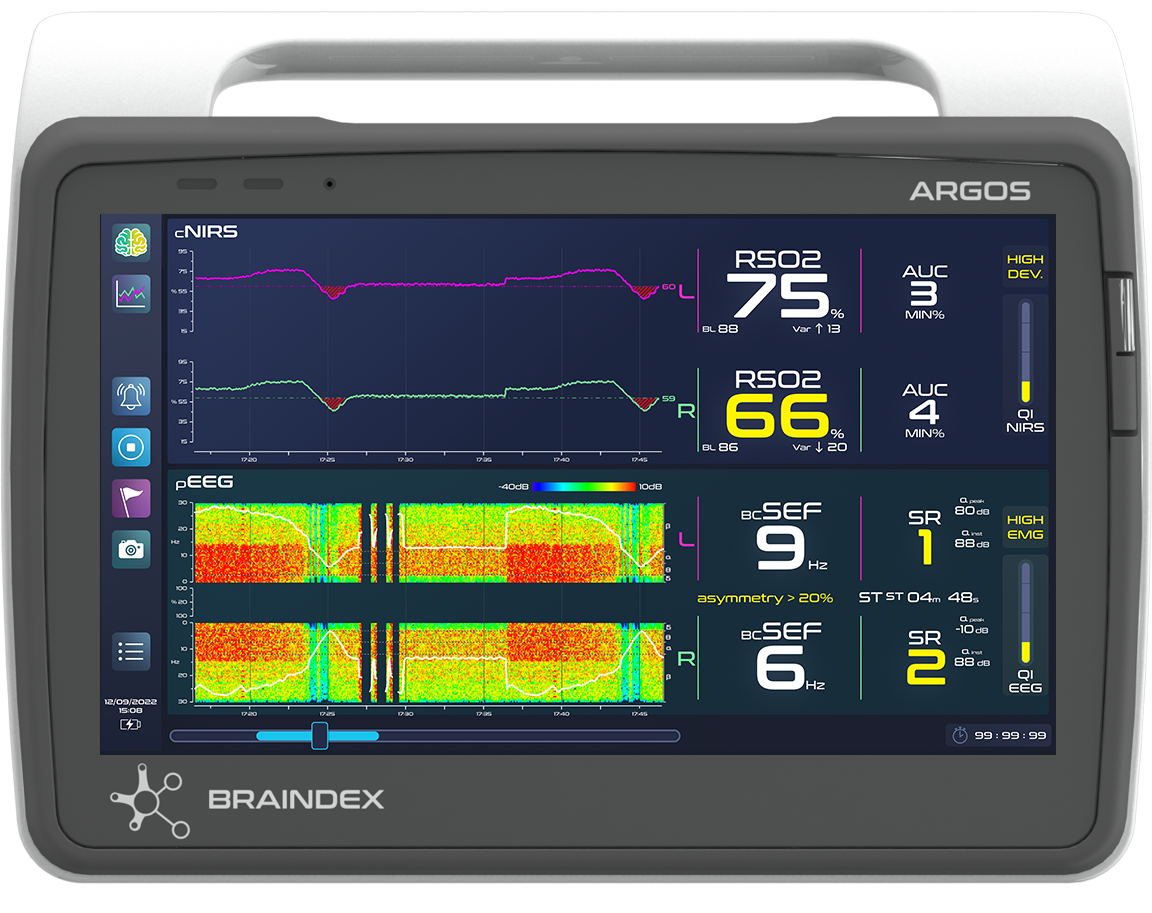

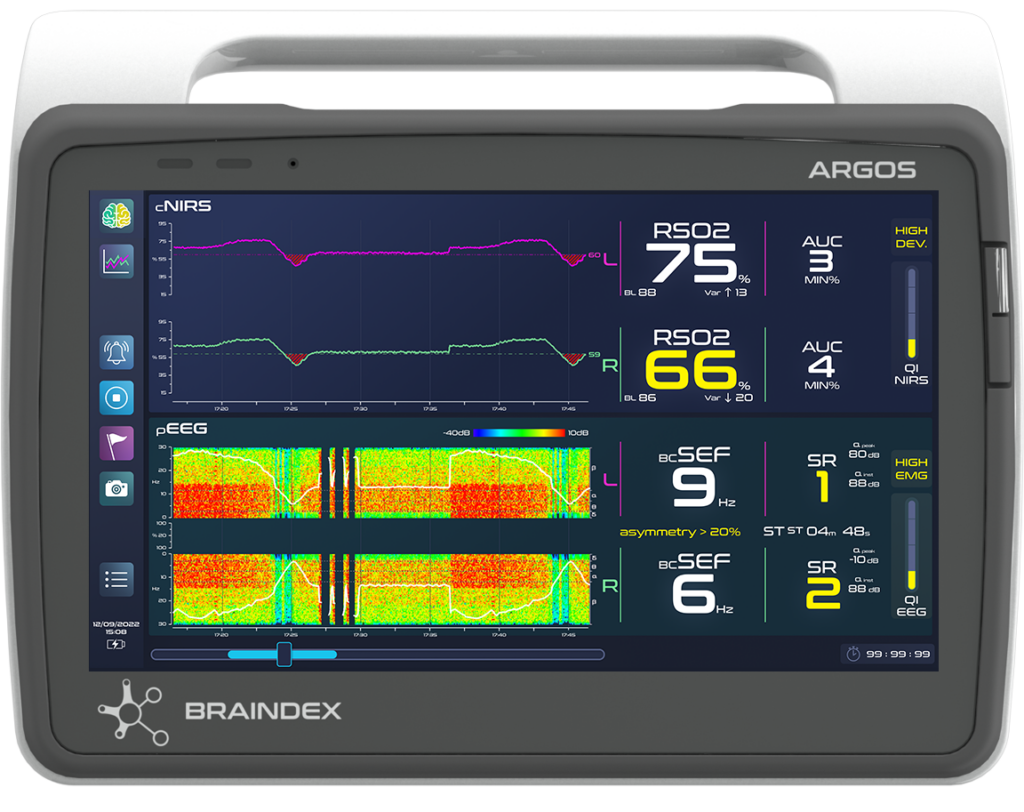
from standard to synergistic displays.




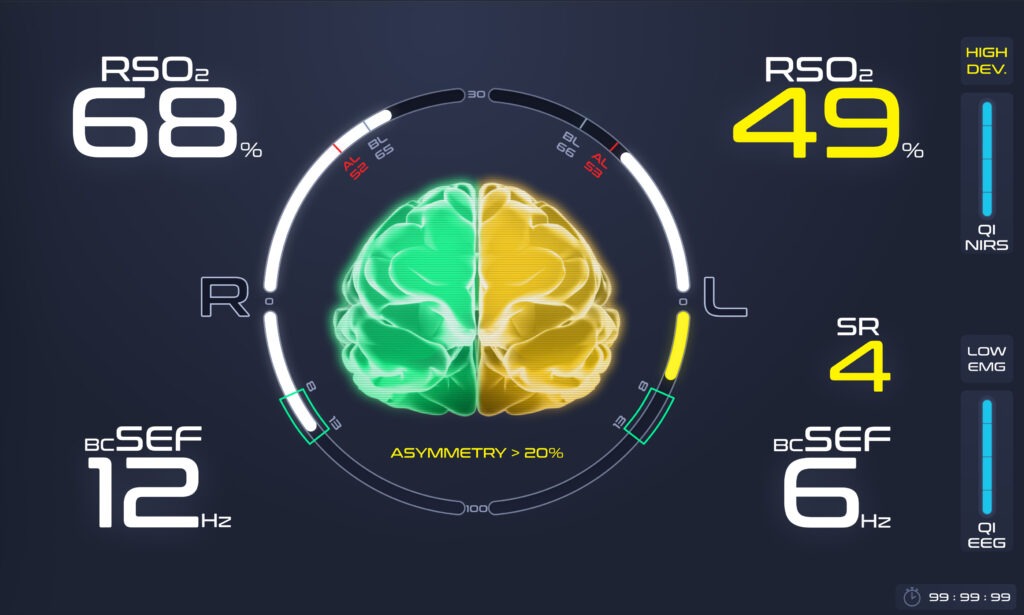
SMART ALERT SYSTEM
The ARGOS Smart Alert system features a disclosed algorithm based on the combination of EEG and NIRS alert thresholds, and a highly visual graphic display of the resulting overall alert level.
The ARGOS Smart Alert system thus automates the identification of potentially dangerous situations for the patient resulting from a combined analysis of EEG and NIRS measurements.
The highly visual graphic display enable clinicians to be rapidly informed for appropriate clinical decision-making to personalized care.
CASE REPORT & BRAIN STRESS INDEX (BSI)
The ARGOS platform provides clinicians with a detailed report for each patient, based on cumulative and temporally derived EEG and NIRS parameters (area under the curve, suppression time, alpha wave peak…).
In addition, ARGOS report provides clinicians with a unique Brain Stress Index, reflecting the total time spent by the patient during surgery under cumulative conditions of oversedation and low cerebral oxygen levels.
The ARGOS BSI provides uniquely objective assessment of an anesthesia contribution to the complex genesis of postoperative neurological complications, paving the way for their anticipation and early treatment.

